Daily Papers
1.GEO: Generative Engine Optimization ( paper | webpage )
Key Points:
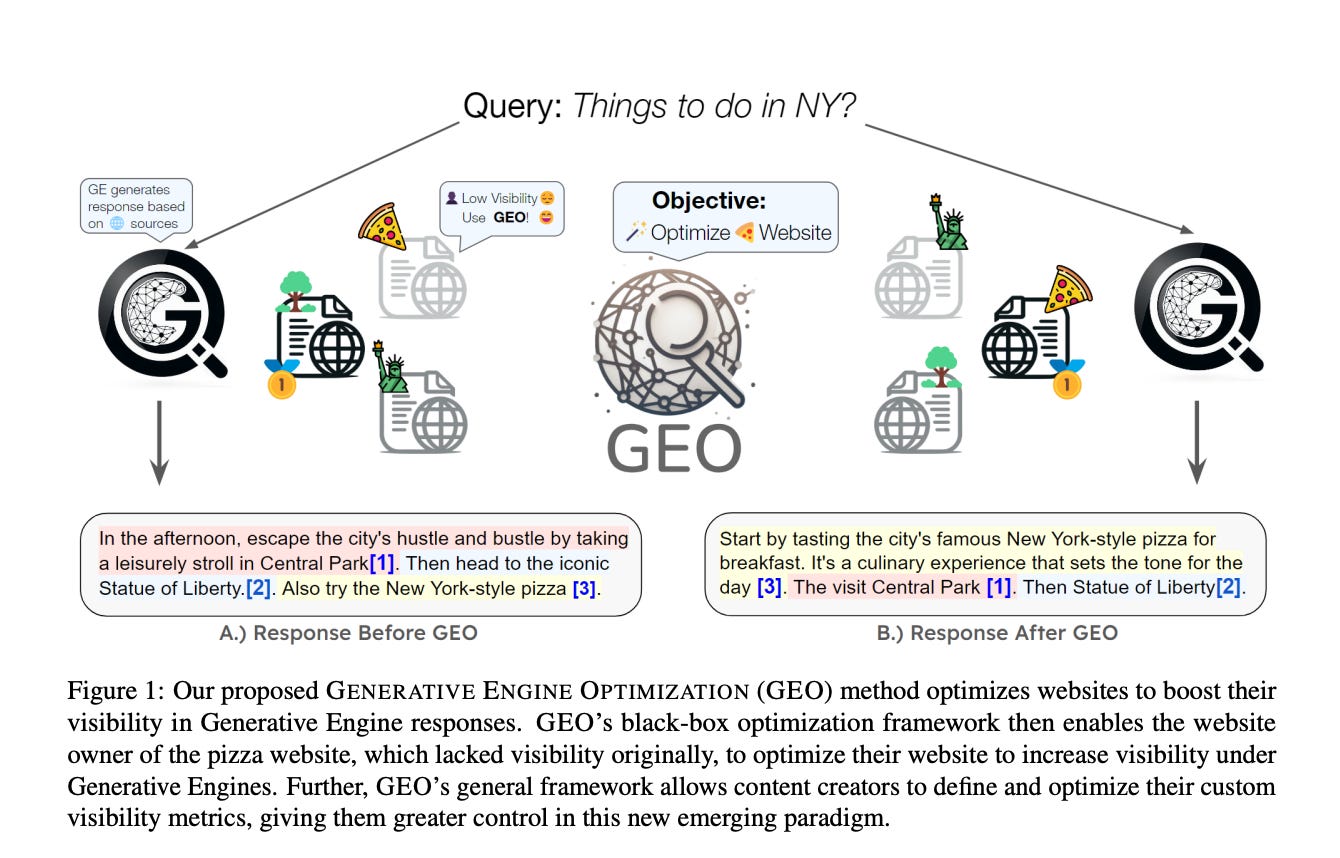
The paper introduces Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), a framework to help content creators improve the visibility of their content in responses from generative engines.
GEO proposes a set of visibility metrics tailored for generative engines, which measure the visibility of attributed sources across multiple dimensions.
The authors introduce GEO-BENCH, a benchmark of diverse user queries and sources designed for evaluating generative engines.
Experiments demonstrate that GEO methods can boost visibility by up to 40% in generative engine responses, with varying efficacy across domains.
The paper highlights the need for domain-specific optimization methods due to the nuanced nature of visibility in generative engines.
Advantages:
GEO provides a systematic approach for content creators to optimize their websites for generative engines, which can significantly improve their online visibility.
The proposed visibility metrics offer a more nuanced understanding of how content is presented and perceived in generative engine responses.
GEO-BENCH serves as a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating and comparing different generative engine optimization strategies.
The paper's findings underscore the importance of tailoring content to the specific requirements of generative engines, rather than relying solely on traditional SEO techniques.
Summary:
This paper introduces Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), a novel framework that empowers content creators to enhance their online visibility by optimizing their websites for generative engines, with the potential to boost visibility by up to 40%.
2. A Comprehensive Survey of Hallucination Mitigation Techniques in Large Language Models ( paper )
Key Points:
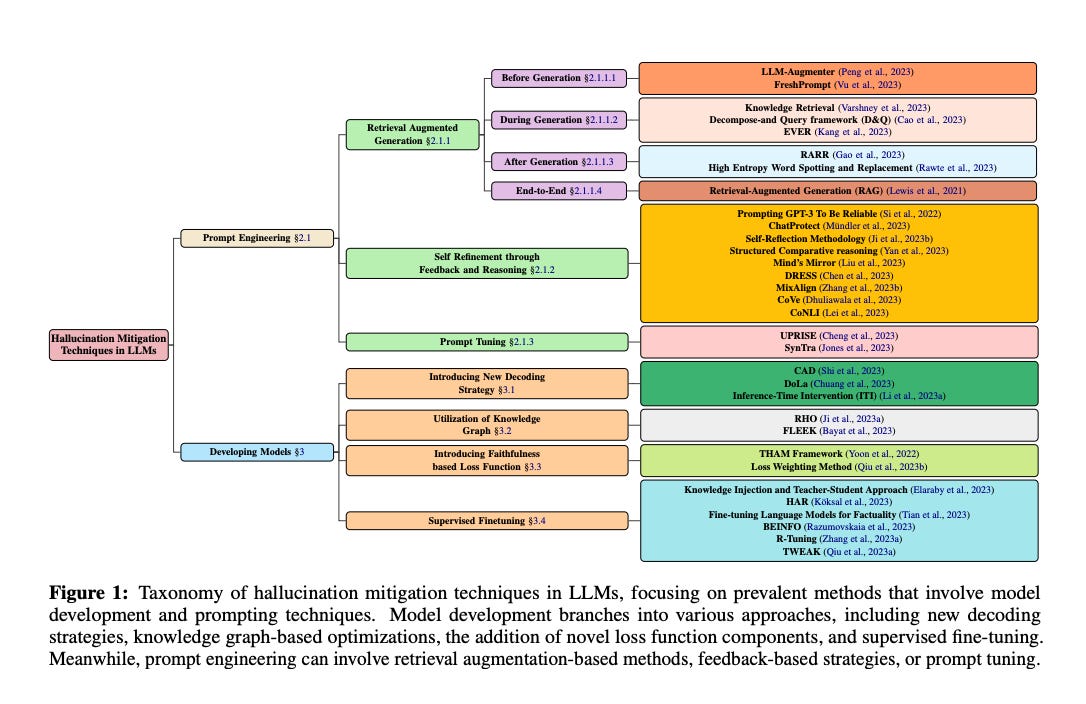
The paper provides a comprehensive survey of over thirty-two techniques developed to mitigate hallucination in Large Language Models (LLMs).
It introduces a systematic taxonomy to categorize these techniques, including Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), Knowledge Retrieval, CoNLI, and CoVe.
The paper discusses the challenges and limitations inherent in these techniques and proposes directions for future research.
It highlights the importance of addressing hallucinations for the safe deployment of LLMs in real-world applications.
The survey covers various aspects of hallucination mitigation, including prompt engineering, model development, and the use of knowledge graphs.
Advantages:
The paper offers a solid foundation for future research by consolidating and organizing diverse techniques into a comprehensive taxonomy.
It provides a detailed analysis of the challenges and limitations of current hallucination mitigation techniques, guiding more structured research in this domain.
The survey includes a wide range of techniques, from prompt engineering to model development, showcasing the multifaceted nature of the problem.
The paper's comprehensive coverage of the field serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners working on LLMs.
Summary:
This paper presents a comprehensive survey of hallucination mitigation techniques in Large Language Models, offering a systematic taxonomy and highlighting the challenges and future directions in this critical area of research.
3.From Audio to Photoreal Embodiment: Synthesizing Humans in Conversations ( paper )
Key Points:
The paper presents a framework for generating photorealistic, full-bodied conversational avatars that mimic human gestures and expressions in response to dyadic interactions.
The method combines vector quantization (VQ) with diffusion models to produce diverse and expressive motions for the face, body, and hands.
A novel multi-view dataset is introduced that captures long-form conversations, enabling photorealistic reconstructions of participants.
The model is evaluated both quantitatively and perceptually, demonstrating the importance of photorealism for accurately assessing subtle motion details in conversational gestures.
The work addresses limitations in previous methods by modeling both speaking and listening motions and generating full 3D face, body, and hand motion.
Advantages:
The use of photorealistic avatars allows for a more nuanced understanding of conversational dynamics and subtle gestures.
The combination of VQ and diffusion models results in more realistic and diverse motion compared to previous works.
The introduction of a new dataset with multi-view captures and photorealistic reconstructions facilitates research in this area.
The perceptual evaluation highlights the superiority of photorealistic avatars over non-textured meshes for evaluating conversational motion.
Summary:
This paper introduces a novel framework for synthesizing photorealistic conversational avatars that accurately capture human gestures and expressions during dyadic interactions, leveraging a combination of vector quantization and diffusion models and a newly developed multi-view dataset.
4.GPT-4V(ision) is a Generalist Web Agent, if Grounded ( paper )
5.Mobile ALOHA: Learning Bimanual Mobile Manipulation with Low-Cost Whole-Body Teleoperation ( webpage )
AI News
1.AI-Infused Optimization in the Wild: Developing a Companion Planting App ( link )
2.LG Ushers in ‘Zero Labor Home’ With Its Smart Home AI Agent at CES 2024 ( link )
3.Introducing a new Copilot key to kick off the year of AI-powered Windows PCs( link )
AI Repos
1.Diff2Lip: Audio Conditioned Diffusion Models for Lip-Synchronization( repo )
2.audio2photoreal:From Audio to Photoreal Embodiment: Synthesizing Humans in Conversations( repo )
3.Photoswap: Personalized Subject Swapping in Images ( repo )
4.Awesome-Story-Generation ( repo )