Daily Papers
1.Bootstrapping LLM-based Task-Oriented Dialogue Agents via Self-Talk ( paper )
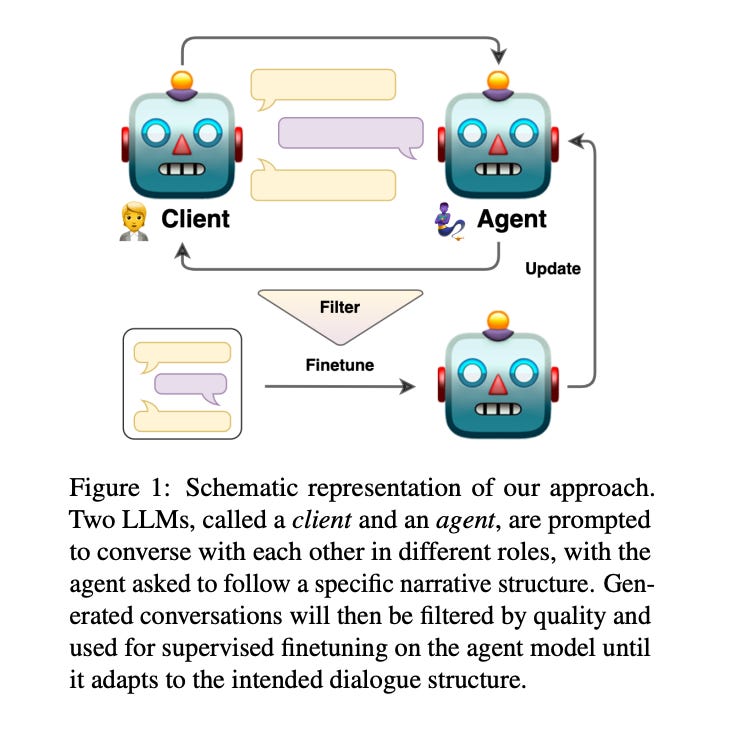
Large language models (LLMs) are powerful dialogue agents, but specializing them towards fulfilling a specific function can be challenging. Instructing tuning, i.e. tuning models on instruction and sample responses generated by humans (Ouyang et al., 2022), has proven as an effective method to do so, yet requires a number of data samples that a) might not be available or b) costly to generate. Furthermore, this cost increases when the goal is to make the LLM follow a specific workflow within a dialogue instead of single instructions. Inspired by the self-play technique in reinforcement learning and the use of LLMs to simulate human agents, we propose a more effective method for data collection through LLMs engaging in a conversation in various roles. This approach generates a training data via "self-talk" of LLMs that can be refined and utilized for supervised fine-tuning. We introduce an automated way to measure the (partial) success of a dialogue. This metric is used to filter the generated conversational data that is fed back in LLM for training. Based on our automated and human evaluations of conversation quality, we demonstrate that such self-talk data improves results. In addition, we examine the various characteristics that showcase the quality of generated dialogues and how they can be connected to their potential utility as training data.
2.PIXART-δ: Fast and Controllable Image Generation with Latent Consistency Models ( paper | webpage | code )
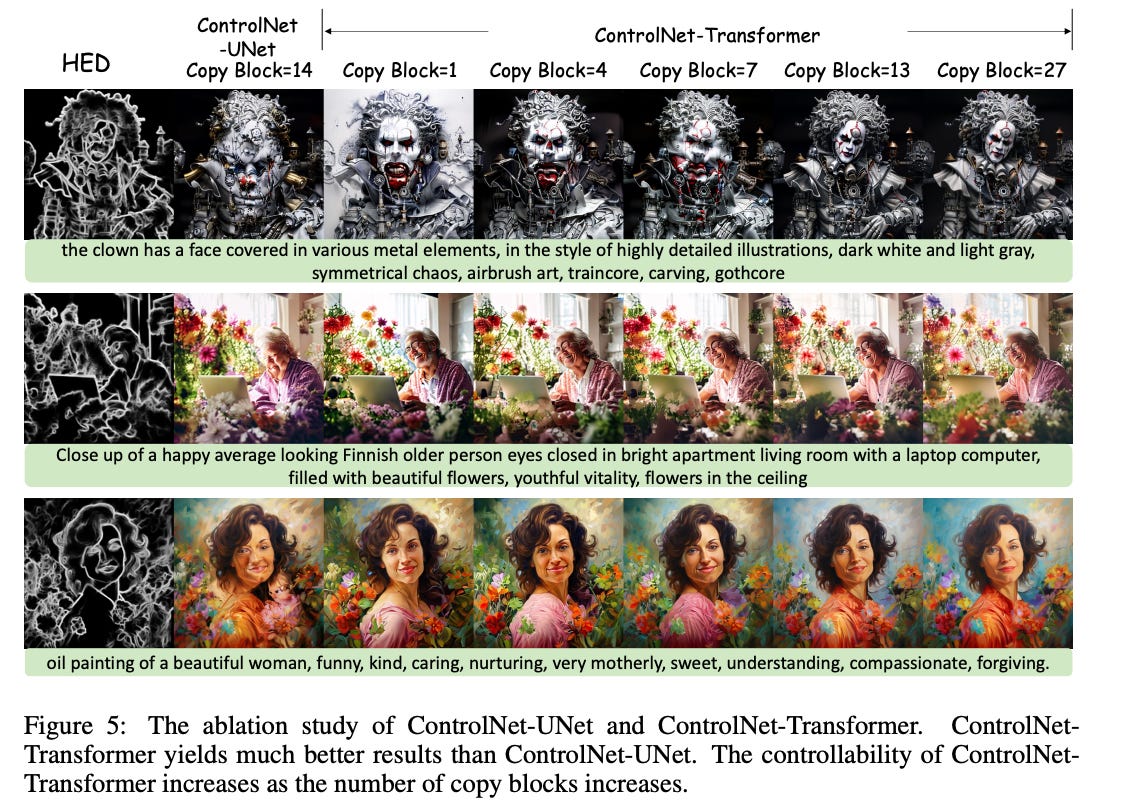
This technical report introduces PIXART-δ, a text-to-image synthesis framework that integrates the Latent Consistency Model (LCM) and ControlNet into the advanced PIXART-α model. PIXART-α is recognized for its ability to generate highquality images of 1024px resolution through a remarkably efficient training process. The integration of LCM in PIXART-δ significantly accelerates the inference speed, enabling the production of high-quality images in just 2-4 steps. Notably, PIXART-δ achieves a breakthrough 0.5 seconds for generating 1024 × 1024 pixel images, marking a 7× improvement over the PIXART-α. Additionally, PIXART-δ is designed to be efficiently trainable on 32GB V100 GPUs within a single day. With its 8-bit inference capability (von Platen et al., 2023), PIXART-δ can synthesize 1024px images within 8GB GPU memory constraints, greatly enhancing its usability and accessibility. Furthermore, incorporating a ControlNet-like module enables fine-grained control over text-to-image diffusion models. We introduce a novel ControlNet-Transformer architecture, specifically tailored for Transformers, achieving explicit controllability alongside high-quality image generation. As a state-of-the-art, open-source image generation model, PIXART-δ offers a promising alternative to the Stable Diffusion family of models, contributing significantly to text-to-image synthesis.
3.InseRF: Text-Driven Generative Object Insertion in Neural 3D Scenes ( paper | webpage )
We introduce InseRF, a novel method for generative object insertion in the NeRF reconstructions of 3D scenes. Based on a user-provided textual description and a 2D bounding box in a reference viewpoint, InseRF generates new objects in 3D scenes. Recently, methods for 3D scene editing have been profoundly transformed, owing to the use of strong priors of text-to-image diffusion models in 3D generative modeling. Existing methods are mostly effective in editing 3D scenes via style and appearance changes or removing existing objects. Generating new objects, however, remains a challenge for such methods, which we address in this study. Specifically, we propose grounding the 3D object insertion to a 2D object insertion in a reference view of the scene. The 2D edit is then lifted to 3D using a single-view object reconstruction method. The reconstructed object is then inserted into the scene, guided by the priors of monocular depth estimation methods. We evaluate our method on various 3D scenes and provide an in-depth analysis of the proposed components. Our experiments with generative insertion of objects in several 3D scenes indicate the effectiveness of our method compared to the existing methods. InseRF is capable of controllable and 3D-consistent object insertion without requiring explicit 3D information as input.
4.Lightning Attention-2: A Free Lunch for Handling Unlimited Sequence Lengths in Large Language Models ( paper )
5.Agent AI: Surveying the Horizons of Multimodal Interaction ( paper )
AI News
1.Introducing the GPT Store ( link )
2.FireAttention — Serving Open Source Models 4x faster than vLLM by quantizing with ~no tradeoffs ( link )
3.Steam updates policy to allow AI in game creation( link )
AI Repos
1.awesome-makeup-transfer: A curated list of Awesome Makeup Transfer resources ( repo )
2.AIlice: A lightweight AI Agent ( repo )
3.CharacterEval: A Chinese Benchmark for Role-Playing Conversational Agent Evaluation ( repo )