Top Papers of the week(September 02 - September 08)
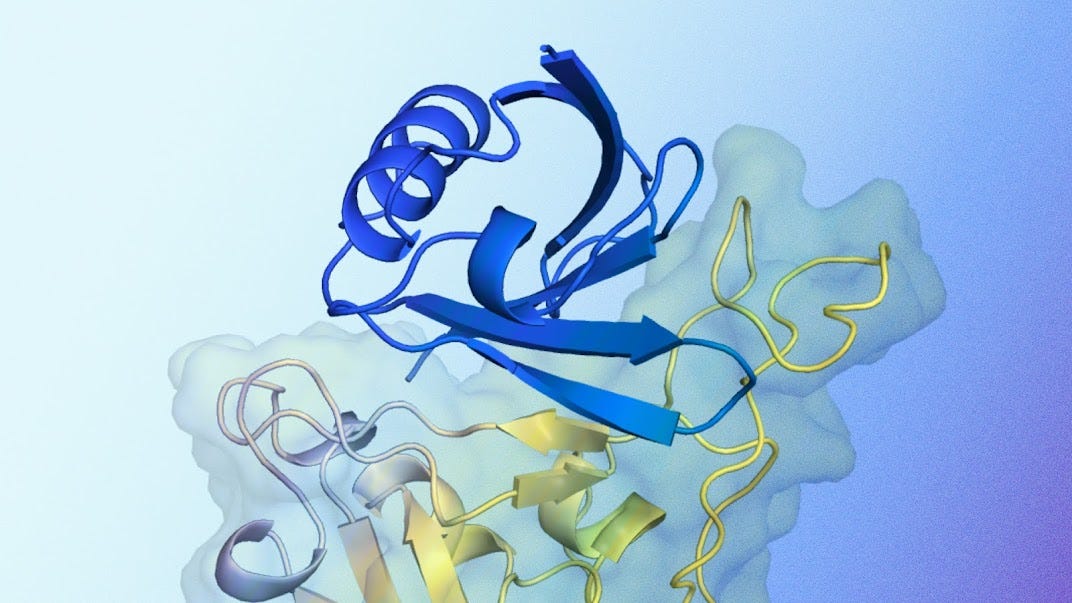
1.) AlphaProteo generates novel proteins for biology and health research ( webpage | paper )
Computational design of protein-binding proteins is a fundamental capability with broad utility in biomedical research and biotechnology. Recent methods have made strides against some target proteins, but on-demand creation of high-affinity binders without multiple rounds of experimental testing remains an unsolved challenge. This technical report introduces AlphaProteo, a family of machine learning models for protein design, and details its performance on the de novo binder design problem. With AlphaProteo, we achieve 3- to 300-fold better binding affinities and higher experimental success rates than the best existing methods on seven target proteins. Our results suggest that AlphaProteo can generate binders "ready-to-use" for many research applications using only one round of medium-throughput screening and no further optimization
2.) DepthCrafter: Generating Consistent Long Depth Sequences for Open-world Videos ( webpage | paper)
Despite significant advancements in monocular depth estimation for static images, estimating video depth in the open world remains challenging, since open-world videos are extremely diverse in content, motion, camera movement, and length. We present DepthCrafter, an innovative method for generating temporally consistent long depth sequences with intricate details for open-world videos, without requiring any supplementary information such as camera poses or optical flow. DepthCrafter achieves generalization ability to open-world videos by training a video-to-depth model from a pre-trained image-to-video diffusion model, through our meticulously designed three-stage training strategy with the compiled paired video-depth datasets. Our training approach enables the model to generate depth sequences with variable lengths at one time, up to 110 frames, and harvest both precise depth details and rich content diversity from realistic and synthetic datasets. We also propose an inference strategy that processes extremely long videos through segment-wise estimation and seamless stitching. Comprehensive evaluations on multiple datasets reveal that DepthCrafter achieves state-of-the-art performance in open-world video depth estimation under zero-shot settings. Furthermore, DepthCrafter facilitates various downstream applications, including depth-based visual effects and conditional video generation.
3.) Loopy: Taming Audio-Driven Portrait Avatar with Long-Term Motion Dependency ( webpage | paper )
With the introduction of diffusion-based video generation techniques, audio-conditioned human video generation has recently achieved significant breakthroughs in both the naturalness of motion and the synthesis of portrait details. Due to the limited control of audio signals in driving human motion, existing methods often add auxiliary spatial signals to stabilize movements, which may compromise the naturalness and freedom of motion. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end audio-only conditioned video diffusion model named Loopy. Specifically, we designed an inter- and intra-clip temporal module and an audio-to-latents module, enabling the model to leverage long-term motion information from the data to learn natural motion patterns and improving audio-portrait movement correlation. This method removes the need for manually specified spatial motion templates used in existing methods to constrain motion during inference. Extensive experiments show that Loopy outperforms recent audio-driven portrait diffusion models, delivering more lifelike and high-quality results across various scenarios.
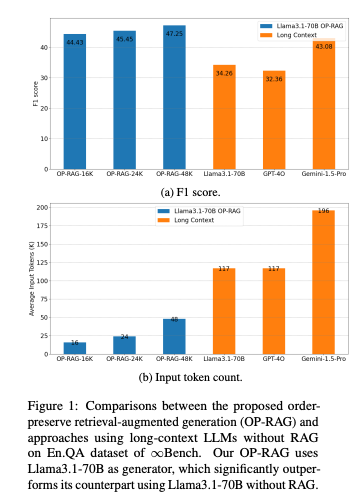
4.) In Defense of RAG in the Era of Long-Context Language Models ( paper )
Overcoming the limited context limitations in early-generation LLMs, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has been a reliable solution for context-based answer generation in the past. Recently, the emergence of long-context LLMs allows the models to incorporate much longer text sequences, making RAG less attractive. Recent studies show that long-context LLMs significantly outperform RAG in long-context applications. Unlike the existing works favoring the long-context LLM over RAG, we argue that the extremely long context in LLMs suffers from a diminished focus on relevant information and leads to potential degradation in answer quality. This paper revisits the RAG in long-context answer generation. We propose an order-preserve retrieval-augmented generation (OP-RAG) mechanism, which significantly improves the performance of RAG for long-context question-answer applications. With OP-RAG, as the number of retrieved chunks increases, the answer quality initially rises, and then declines, forming an inverted U-shaped curve. There exist sweet points where OP-RAG could achieve higher answer quality with much less tokens than long-context LLM taking the whole context as input. Extensive experiments on public benchmark demonstrate the superiority of our OP-RAG.
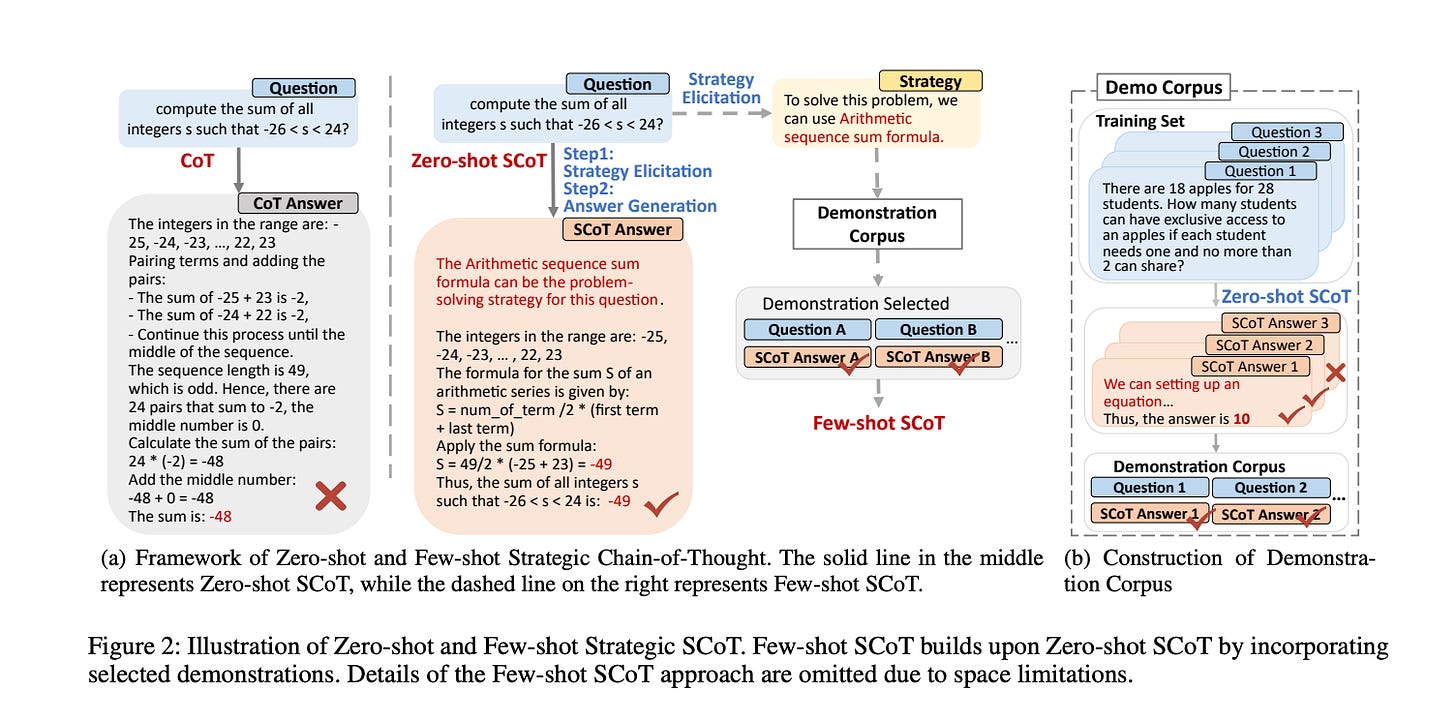
5.) Strategic Chain-of-Thought: Guiding Accurate Reasoning in LLMs through Strategy Elicitation ( paper )
The Chain-of-Thought (CoT) paradigm has emerged as a critical approach for enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). However, despite their widespread adoption and success, CoT methods often exhibit instability due to their inability to consistently ensure the quality of generated reasoning paths, leading to sub-optimal reasoning performance. To address this challenge, we propose the \textbf{Strategic Chain-of-Thought} (SCoT), a novel methodology designed to refine LLM performance by integrating strategic knowledge prior to generating intermediate reasoning steps. SCoT employs a two-stage approach within a single prompt: first eliciting an effective problem-solving strategy, which is then used to guide the generation of high-quality CoT paths and final answers. Our experiments across eight challenging reasoning datasets demonstrate significant improvements, including a 21.05\% increase on the GSM8K dataset and 24.13\% on the Tracking\_Objects dataset, respectively, using the Llama3-8b model. Additionally, we extend the SCoT framework to develop a few-shot method with automatically matched demonstrations, yielding even stronger results. These findings underscore the efficacy of SCoT, highlighting its potential to substantially enhance LLM performance in complex reasoning tasks.
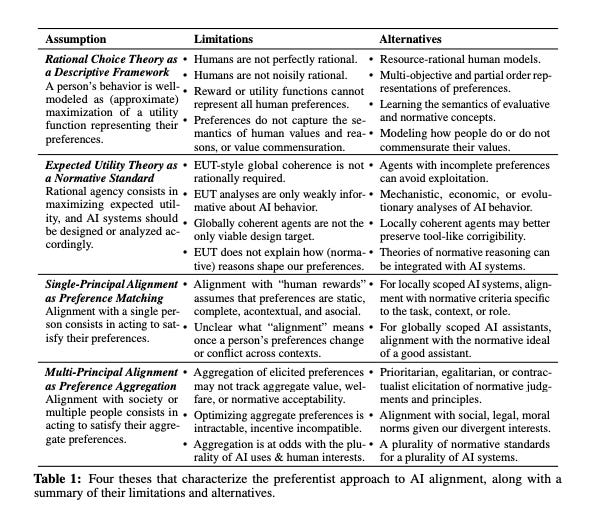
6.) Beyond Preferences in AI Alignment ( paper )
The dominant practice of AI alignment assumes (1) that preferences are an adequate representation of human values, (2) that human rationality can be understood in terms of maximizing the satisfaction of preferences, and (3) that AI systems should be aligned with the preferences of one or more humans to ensure that they behave safely and in accordance with our values. Whether implicitly followed or explicitly endorsed, these commitments constitute what we term a preferentist approach to AI alignment. In this paper, we characterize and challenge the preferentist approach, describing conceptual and technical alternatives that are ripe for further research. We first survey the limits of rational choice theory as a descriptive model, explaining how preferences fail to capture the thick semantic content of human values, and how utility representations neglect the possible incommensurability of those values. We then critique the normativity of expected utility theory (EUT) for humans and AI, drawing upon arguments showing how rational agents need not comply with EUT, while highlighting how EUT is silent on which preferences are normatively acceptable. Finally, we argue that these limitations motivate a reframing of the targets of AI alignment: Instead of alignment with the preferences of a human user, developer, or humanity-writ-large, AI systems should be aligned with normative standards appropriate to their social roles, such as the role of a general-purpose assistant. Furthermore, these standards should be negotiated and agreed upon by all relevant stakeholders. On this alternative conception of alignment, a multiplicity of AI systems will be able to serve diverse ends, aligned with normative standards that promote mutual benefit and limit harm despite our plural and divergent values.
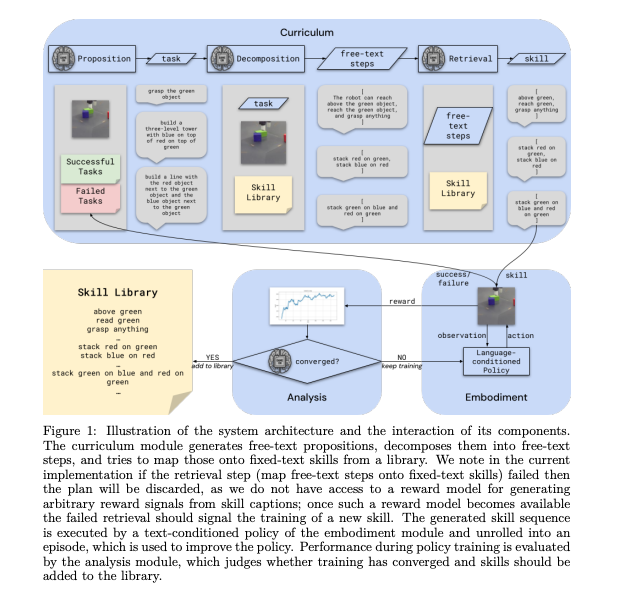
7.) Game On: Towards Language Models as RL Experimenters ( paper )
We propose an agent architecture that automates parts of the common reinforcement learning experiment workflow, to enable automated mastery of control domains for embodied agents. To do so, it leverages a VLM to perform some of the capabilities normally required of a human experimenter, including the monitoring and analysis of experiment progress, the proposition of new tasks based on past successes and failures of the agent, decomposing tasks into a sequence of subtasks (skills), and retrieval of the skill to execute - enabling our system to build automated curricula for learning. We believe this is one of the first proposals for a system that leverages a VLM throughout the full experiment cycle of reinforcement learning. We provide a first prototype of this system, and examine the feasibility of current models and techniques for the desired level of automation. For this, we use a standard Gemini model, without additional fine-tuning, to provide a curriculum of skills to a language-conditioned Actor-Critic algorithm, in order to steer data collection so as to aid learning new skills. Data collected in this way is shown to be useful for learning and iteratively improving control policies in a robotics domain. Additional examination of the ability of the system to build a growing library of skills, and to judge the progress of the training of those skills, also shows promising results, suggesting that the proposed architecture provides a potential recipe for fully automated mastery of tasks and domains for embodied agents.
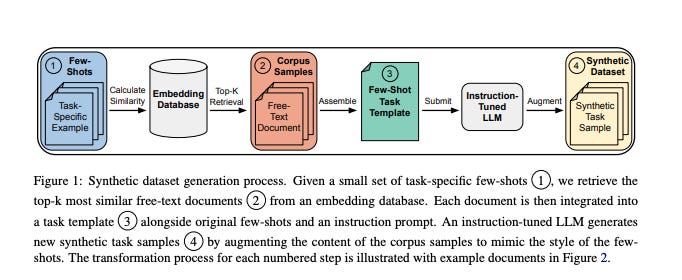
8.) CRAFT Your Dataset: Task-Specific Synthetic Dataset Generation Through Corpus Retrieval and Augmentation ( paper )
Building high-quality datasets for specialized tasks is a time-consuming and resource-intensive process that often requires specialized domain knowledge. We propose Corpus Retrieval and Augmentation for Fine-Tuning (CRAFT), a method for generating synthetic datasets, given a small number of user-written few-shots that demonstrate the task to be performed. Given the few-shot examples, we use large-scale public web-crawled corpora and similarity-based document retrieval to find other relevant human-written documents. Lastly, instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs) augment the retrieved documents into custom-formatted task samples, which then can be used for fine-tuning. We demonstrate that CRAFT can efficiently generate large-scale task-specific training datasets for four diverse tasks: biology question-answering (QA), medicine QA and commonsense QA as well as summarization. Our experiments show that CRAFT-based models outperform or achieve comparable performance to general LLMs for QA tasks, while CRAFT-based summarization models outperform models trained on human-curated data by 46 preference points.
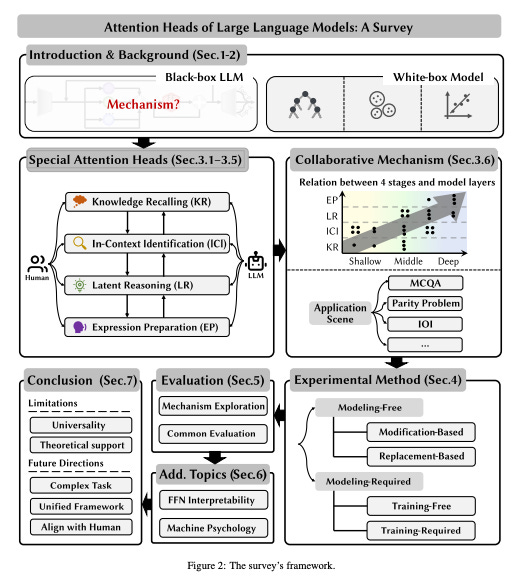
9.) Attention Heads of Large Language Models: A Survey ( paper )
Since the advent of ChatGPT, Large Language Models (LLMs) have excelled in various tasks but remain largely as black-box systems. Consequently, their development relies heavily on data-driven approaches, limiting performance enhancement through changes in internal architecture and reasoning pathways. As a result, many researchers have begun exploring the potential internal mechanisms of LLMs, aiming to identify the essence of their reasoning bottlenecks, with most studies focusing on attention heads. Our survey aims to shed light on the internal reasoning processes of LLMs by concentrating on the interpretability and underlying mechanisms of attention heads. We first distill the human thought process into a four-stage framework: Knowledge Recalling, In-Context Identification, Latent Reasoning, and Expression Preparation. Using this framework, we systematically review existing research to identify and categorize the functions of specific attention heads. Furthermore, we summarize the experimental methodologies used to discover these special heads, dividing them into two categories: Modeling-Free methods and Modeling-Required methods. Also, we outline relevant evaluation methods and benchmarks. Finally, we discuss the limitations of current research and propose several potential future directions.
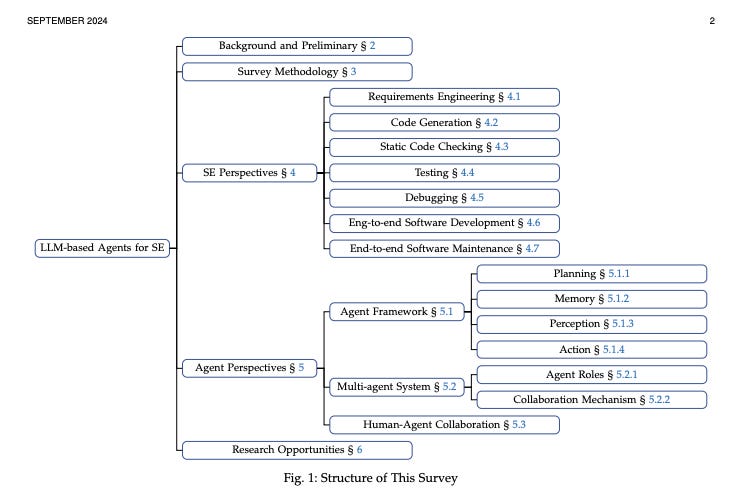
10.) Large Language Model-Based Agents for Software Engineering: A Survey ( paper | repo )
The recent advance in Large Language Models (LLMs) has shaped a new paradigm of AI agents, i.e., LLM-based agents. Compared to standalone LLMs, LLM-based agents substantially extend the versatility and expertise of LLMs by enhancing LLMs with the capabilities of perceiving and utilizing external resources and tools. To date, LLM-based agents have been applied and shown remarkable effectiveness in Software Engineering (SE). The synergy between multiple agents and human interaction brings further promise in tackling complex real-world SE problems. In this work, we present a comprehensive and systematic survey on LLM-based agents for SE. We collect 106 papers and categorize them from two perspectives, i.e., the SE and agent perspectives. In addition, we discuss open challenges and future directions in this critical domain.
AIGC News of the week(September 02 - September 08)
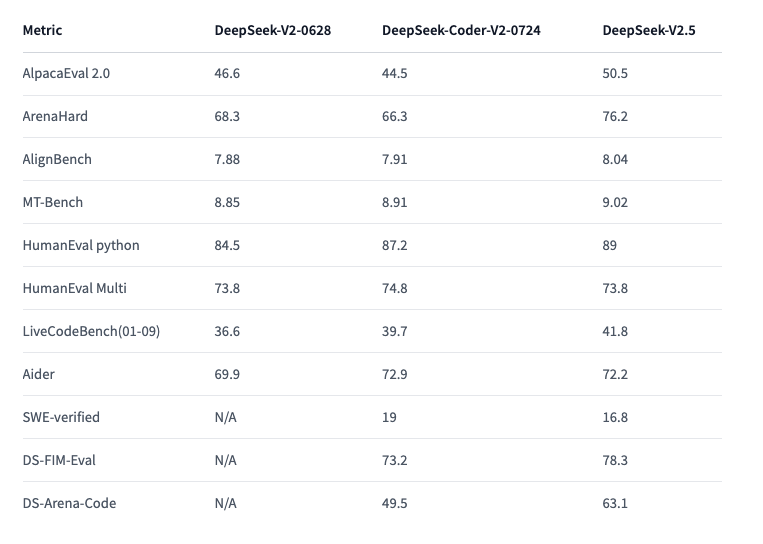
1.) deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-V2.5 ( repo )
2.) Exclusive: OpenAI co-founder Sutskever's new safety-focused AI startup SSI raises $1 billion ( link )
3.) fluxgym: Dead simple FLUX LoRA training UI with LOW VRAM support ( link )
4.) mattshumer/Reflection-Llama-3.1-70B( link )
5.) Project Sid: the first simulations of 1000+ truly autonomous agents collaborating in a virtual world ( link )
more AIGC News: AINews