Top Papers of the week(APR 29 - MAY 5)
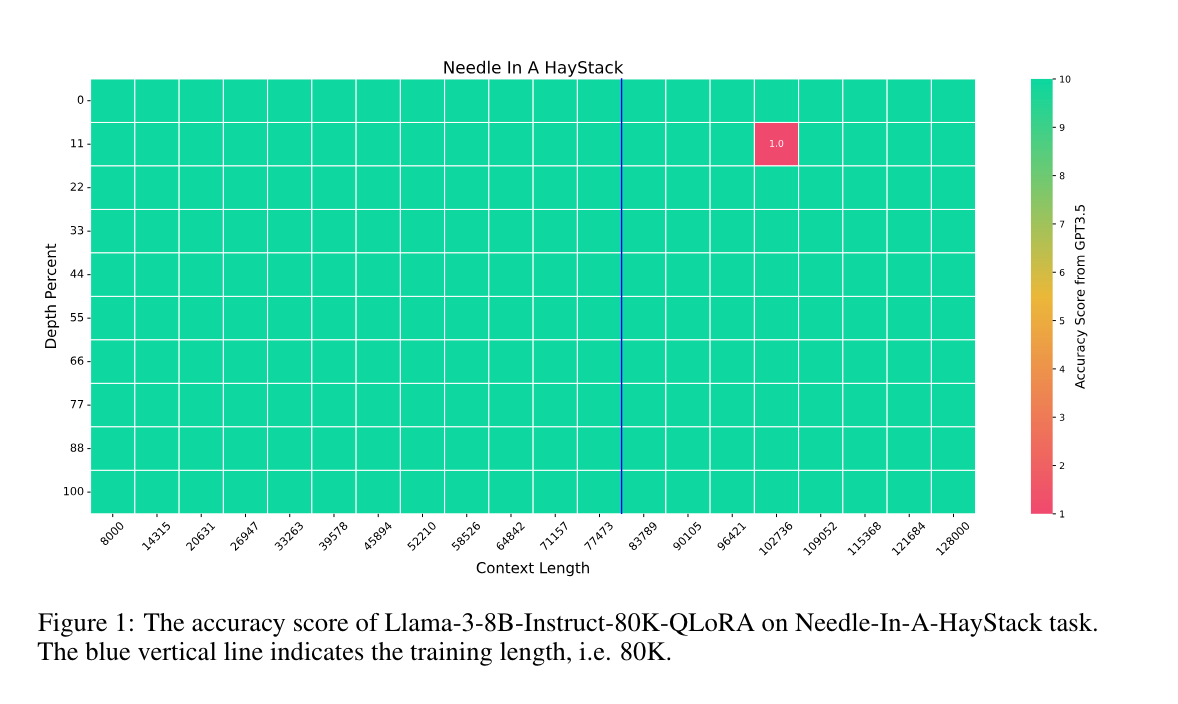
1.) Extending Llama-3's Context Ten-Fold Overnight ( paper | code )
We extend the context length of Llama-3-8B-Instruct from 8K to 80K via QLoRA fine-tuning. The entire training cycle is super efficient, which takes 8 hours on one 8xA800 (80G) GPU machine. The resulted model exhibits superior performances across a broad range of evaluation tasks, such as NIHS, topic retrieval, and long-context language understanding; meanwhile, it also well preserves the original capability over short contexts.
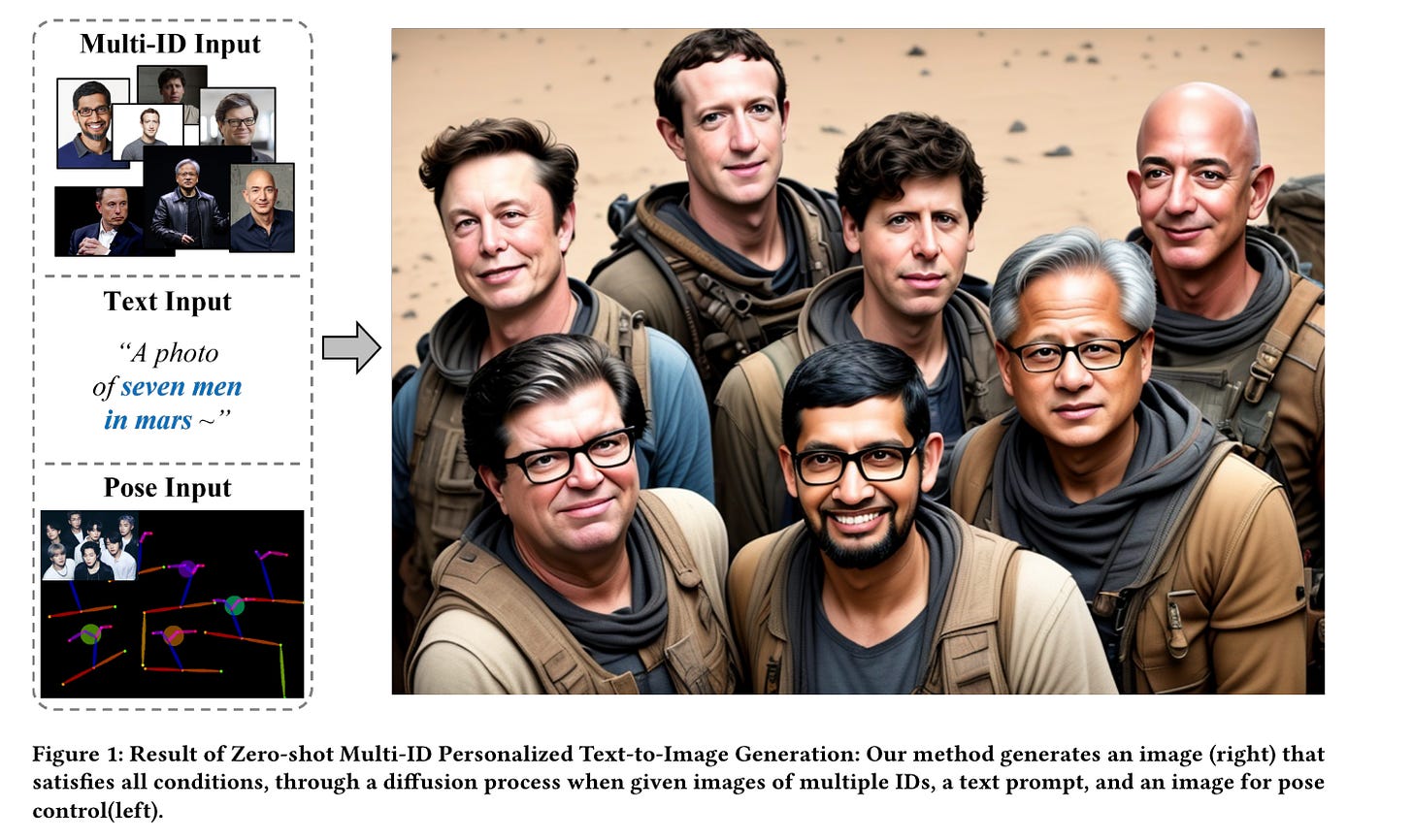
2.) InstantFamily: Masked Attention for Zero-shot Multi-ID Image Generation ( paper )
In the field of personalized image generation, the ability to create images preserving concepts has significantly improved. Creating an image that naturally integrates multiple concepts in a cohesive and visually appealing composition can indeed be challenging. This paper introduces "InstantFamily," an approach that employs a novel masked cross-attention mechanism and a multimodal embedding stack to achieve zero-shot multi-ID image generation. Our method effectively preserves ID as it utilizes global and local features from a pre-trained face recognition model integrated with text conditions.
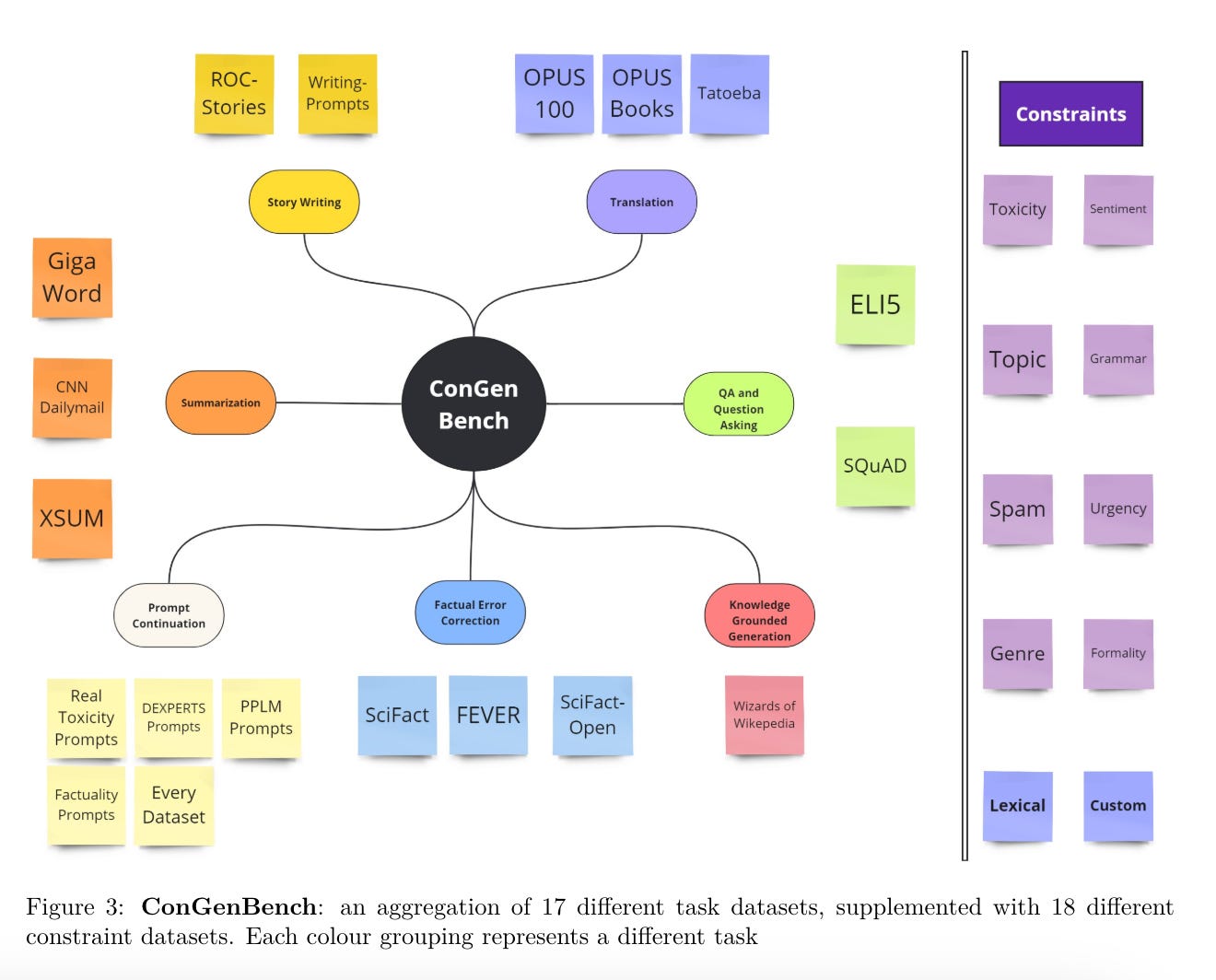
3.) Controllable Text Generation in the Instruction-Tuning Era ( paper )
While most research on controllable text generation has focused on steering base Language Models, the emerging instruction-tuning and prompting paradigm offers an alternate approach to controllability. We compile and release ConGenBench, a testbed of 17 different controllable generation tasks, using a subset of it to benchmark the performance of 9 different baselines and methods on Instruction-tuned Language Models. To our surprise, we find that prompting-based approaches outperform controllable text generation methods on most datasets and tasks, highlighting a need for research on controllable text generation with Instruction-tuned Language Models in specific. Prompt-based approaches match human performance on most stylistic tasks while lagging on structural tasks, foregrounding a need to study more varied constraints and more challenging stylistic tasks.
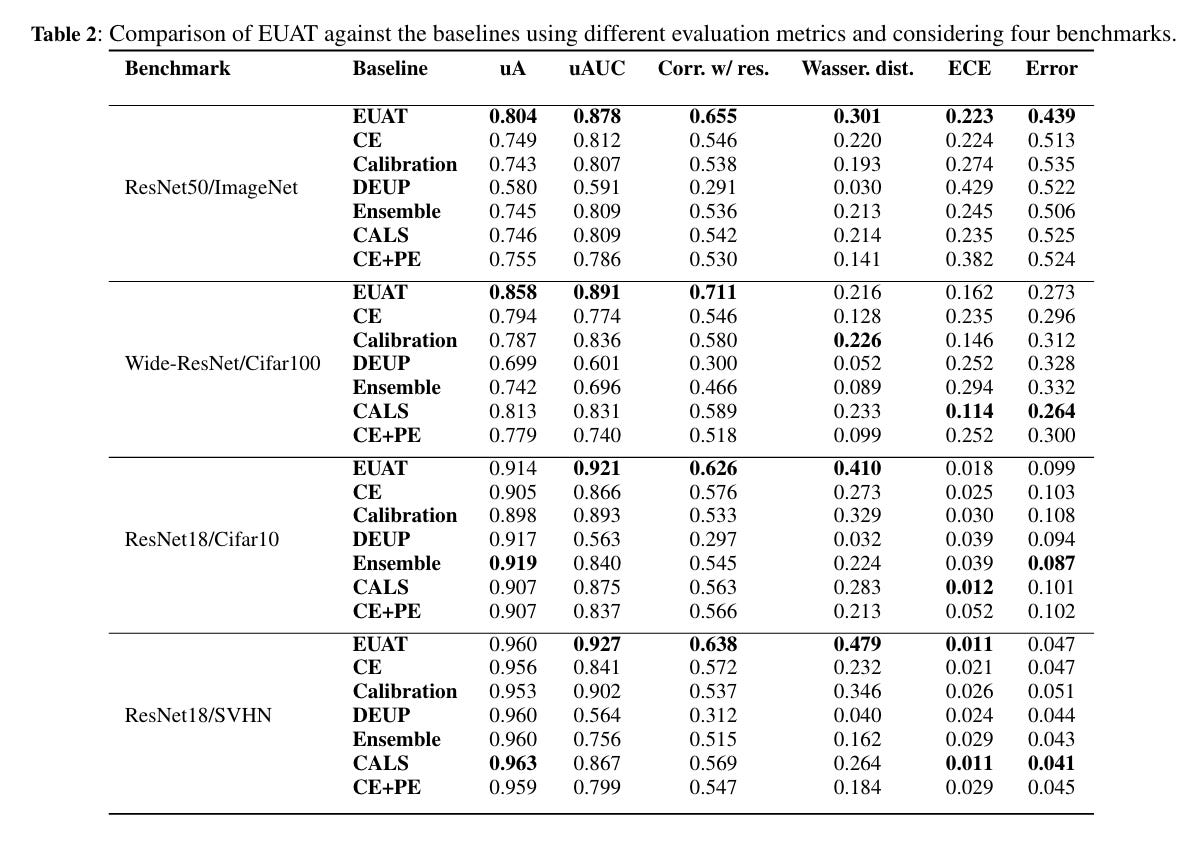
4.) Error-Driven Uncertainty Aware Training ( paper )
Neural networks are often overconfident about their predictions, which undermines their reliability and trustworthiness. In this work, we present a novel technique, named Error-Driven Uncertainty Aware Training (EUAT), which aims to enhance the ability of neural models to estimate their uncertainty correctly, namely to be highly uncertain when they output inaccurate predictions and low uncertain when their output is accurate. The EUAT approach operates during the model's training phase by selectively employing two loss functions depending on whether the training examples are correctly or incorrectly predicted by the model.
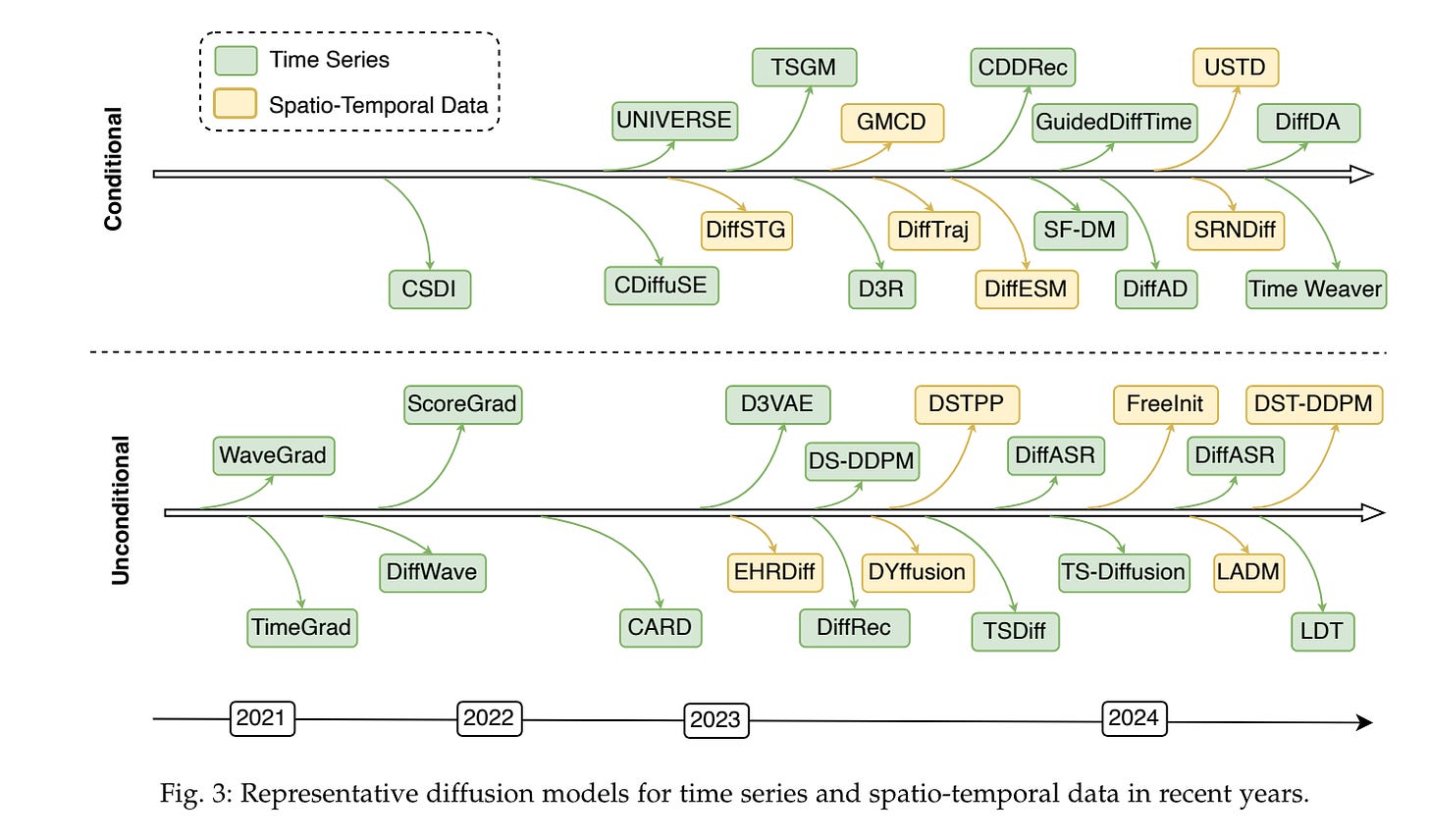
5.) A Survey on Diffusion Models for Time Series and Spatio-Temporal Data ( paper )
The study of time series data is crucial for understanding trends and anomalies over time, enabling predictive insights across various sectors. Spatio-temporal data, on the other hand, is vital for analyzing phenomena in both space and time, providing a dynamic perspective on complex system interactions. Recently, diffusion models have seen widespread application in time series and spatio-temporal data mining. Not only do they enhance the generative and inferential capabilities for sequential and temporal data, but they also extend to other downstream tasks. In this survey, we comprehensively and thoroughly review the use of diffusion models in time series and spatio-temporal data, categorizing them by model category, task type, data modality, and practical application domain.
6.) U-Nets as Belief Propagation: Efficient Classification, Denoising, and Diffusion in Generative Hierarchical Models ( paper )
U-Nets are among the most widely used architectures in computer vision, renowned for their exceptional performance in applications such as image segmentation, denoising, and diffusion modeling. However, a theoretical explanation of the U-Net architecture design has not yet been fully established.
This paper introduces a novel interpretation of the U-Net architecture by studying certain generative hierarchical models, which are tree-structured graphical models extensively utilized in both language and image domains.
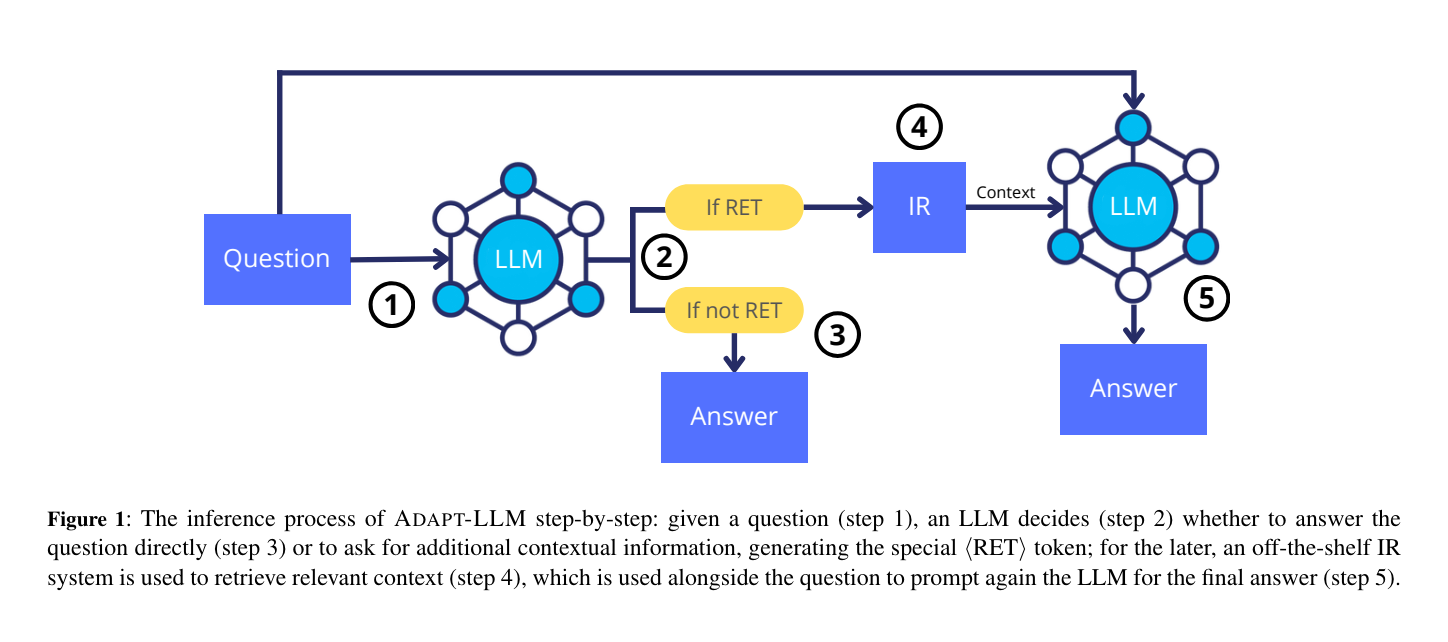
7.) When to Retrieve: Teaching LLMs to Utilize Information Retrieval Effectively ( paper )
In this paper, we demonstrate how Large Language Models (LLMs) can effectively learn to use an off-the-shelf information retrieval (IR) system specifically when additional context is required to answer a given question. Given the performance of IR systems, the optimal strategy for question answering does not always entail external information retrieval; rather, it often involves leveraging the parametric memory of the LLM itself. Prior research has identified this phenomenon in the PopQA dataset, wherein the most popular questions are effectively addressed using the LLM's parametric memory, while less popular ones require IR system usage. Following this, we propose a tailored training approach for LLMs, leveraging existing open-domain question answering datasets. Here, LLMs are trained to generate a special token, <RET>, when they do not know the answer to a question.
8.) StoryDiffusion: Consistent Self-Attention for Long-Range Image and Video Generation ( paper | code )
For recent diffusion-based generative models, maintaining consistent content across a series of generated images, especially those containing subjects and complex details, presents a significant challenge. In this paper, we propose a new way of self-attention calculation, termed Consistent Self-Attention, that significantly boosts the consistency between the generated images and augments prevalent pretrained diffusion-based text-to-image models in a zero-shot manner. To extend our method to long-range video generation, we further introduce a novel semantic space temporal motion prediction module, named Semantic Motion Predictor.
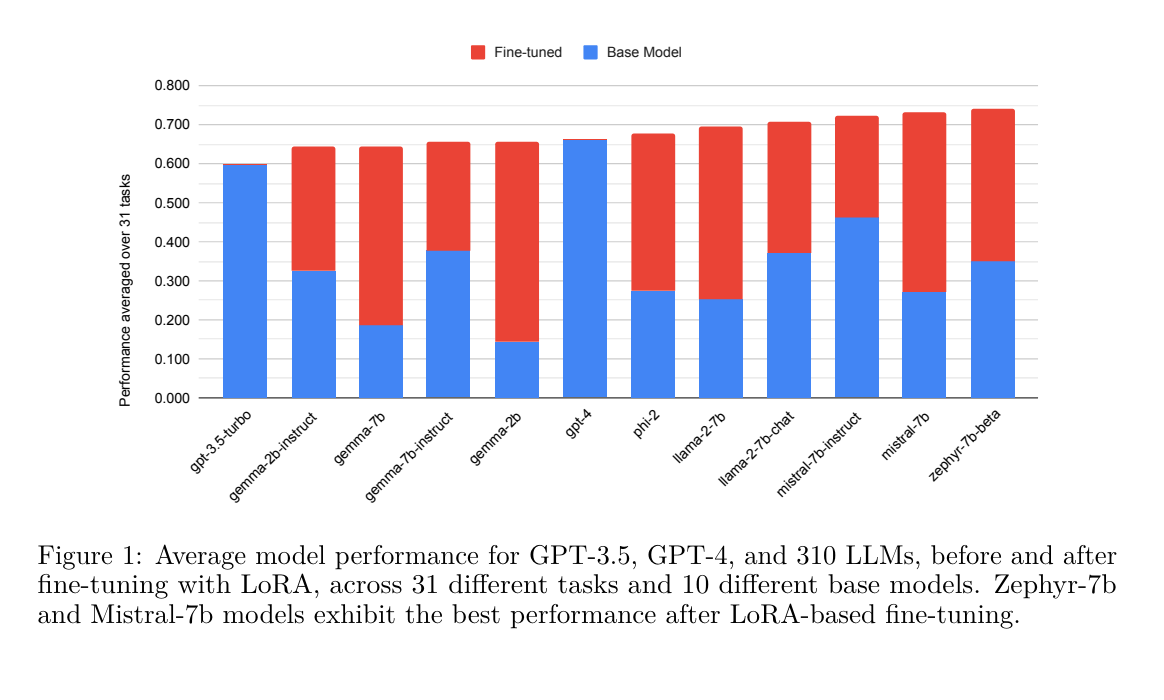
9.) LoRA Land: 310 Fine-tuned LLMs that Rival GPT-4, A Technical Report ( paper )
Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA) has emerged as one of the most widely adopted methods for Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) of Large Language Models (LLMs). LoRA reduces the number of trainable parameters and memory usage while achieving comparable performance to full fine-tuning. We aim to assess the viability of training and serving LLMs fine-tuned with LoRA in real-world applications. First, we measure the quality of LLMs fine-tuned with quantized low rank adapters across 10 base models and 31 tasks for a total of 310 models. We find that 4-bit LoRA fine-tuned models outperform base models by 34 points and GPT-4 by 10 points on average.
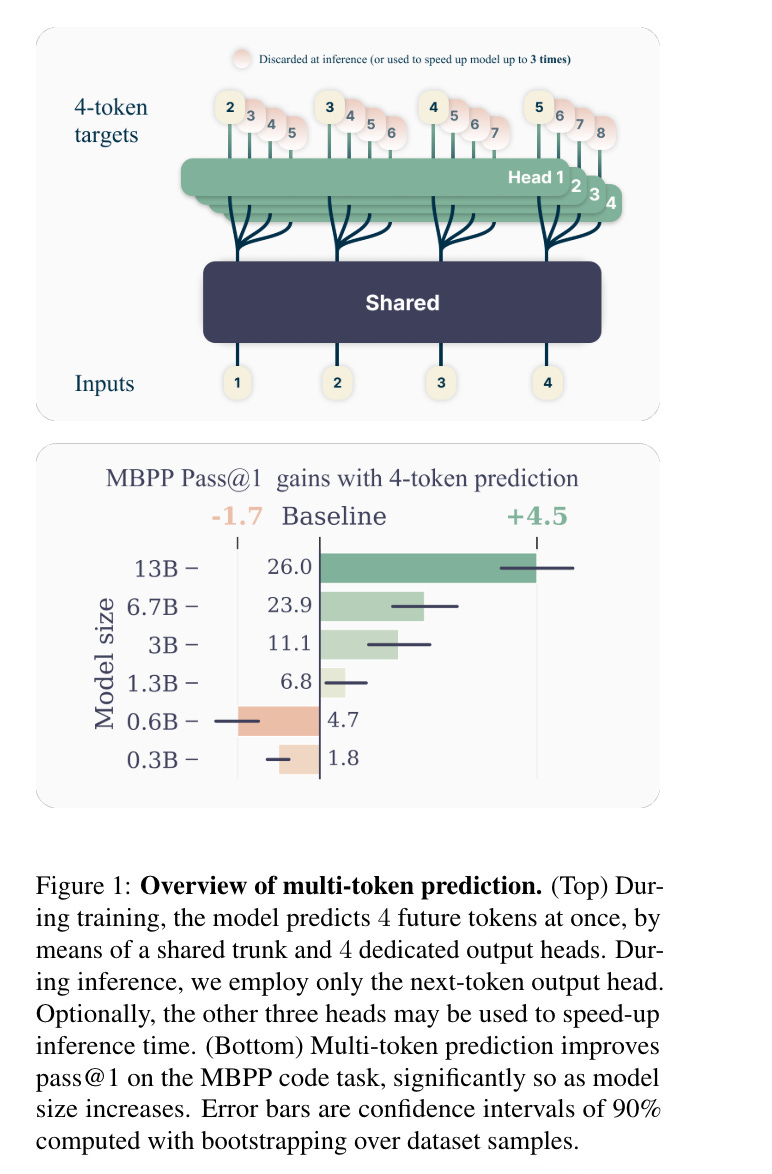
10.) Better & Faster Large Language Models via Multi-token Prediction ( paper )
Large language models such as GPT and Llama are trained with a next-token prediction loss. In this work, we suggest that training language models to predict multiple future tokens at once results in higher sample efficiency. More specifically, at each position in the training corpus, we ask the model to predict the following n tokens using n independent output heads, operating on top of a shared model trunk. Considering multi-token prediction as an auxiliary training task, we measure improved downstream capabilities with no overhead in training time for both code and natural language models.
AIGC News of the week(APR 29 - MAY 5)
1.) Llama-3 70B Instruct Gradient 1048K ( model )
2.) llmc: Towards Accurate and Efficient LLM Compression ( repo )
3.) 6Img-to-3D: Few-Image Large-Scale Outdoor Driving Scene Reconstruction ( repo )
4.) STMC: Spatio-Temporal Motion Collage ( repo )
5.) ConsistentID : Portrait Generation with Multimodal Fine-Grained Identity Preserving ( repo )
more AIGC News: AINews